
Apply to a foreign university with confidence
- Properly fulfilled documents
- Perfect motivation letter
- Support from a personal mentor
- Offers from several universities
Article score: 4 out of 5 (2 reviews)
Education in Denmark is recognized all over the world and is an excellent foundation for a future career, especially in fields such as natural and social sciences, engineering and IT. What are the (dis)advantages of studying in Denmark, how much does it cost and how to get accepted into a Danish university?
Free consultation



Most Danes speak English, so students who come to Denmark do not need to know Danish. About 80% of the population understands English, and some speak German, French or Spanish. However, being able to speak Danish will benefit you both socially and in your job search.
A residence permit for studies is issued to foreign students, and allows its holders to attend free Danish language classes. To do this, you only need to pay a deposit of 303 USD, which is later returned in full. Students who receive government welfare benefits are exempt from paying a deposit. Students are entitled to language studies for 42 months within 5 years after arriving in Denmark.
Language training programs consist of different levels and each of them is divided into modules, which culminate in an official exam. Private, public language centers and many Danish universities offer Danish courses. Programs in universities often take place at the beginning of the academic year or as part of a university summer school.
In Denmark, children go to school at the age of 6-7 and are obliged to study up until they are 15-16. Education takes place in public schools (folkeskole), which are free and open to everyone. Denmark also has a tradition of private schools, attended by about 15% of all primary-level children.
After grade 9, students can go to elective grade 10 (if recommended by the school, to improve grades) or continue their education for several years. The next school level corresponds to ages 16 to 19 and is only required for those who want to go to university. Students can choose one of two paths:
Teenagers wishing to study at the university must choose one of the four educational programs:
| Title | Translation | Direction | Duration |
| HF, Hojere Forberedelseseksamen | Higher Preparatory Examination | Natural and Social Sciences | 2 years |
| HTX, Hojere Teknisk Eksamen | Higher Technical Examination | Mathematics and Engineering | 3 years |
| HHX, Hojere Handelseksamen | Higher Commercial Examination | Trade, Business, Economics | 3 years |
STX, Gymnasium | Gymnasium | Broad program covering different subjects | 3 years |
If students have completed 10 years of basic education, they can study in high school, known as HF only for 2 years. If they studied for 9 years, their studies must last for 3 years (STX, HHX and HTX).
Private schools in Denmark can be roughly divided into the following categories:
There are about 20 such schools, 6% of all high school students study in them. The content of the curriculum is regulated in the same way as in public schools, because education leads to the unified high school exam (Studentereksamen).
Education in Denmark is recognized all over the world and is an excellent foundation for a future career, especially in fields such as natural and social sciences, engineering and IT. Denmark encourages innovation and invests huge sums in education that exceed 6% of the country's GDP[1]. And in terms of the number of Nobel Prizes per capita, Denmark ranks 7th in the world[2]. Thus, the quality of education, advanced Danish culture and a high standard of living attract international students, the number of which has already exceeded 30000 people.
| Type of study | Age | Duration | Min. cost | Avg. cost | Min. language proficiency | Exams |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer camp | 6+ | 1-7 weeks | 151 USD/week | 227 USD/week | - | - |
| Language courses | 7+ | 1-52 weeks | Free | 227 USD/month | A1 | Conducted by schools |
| Secondary education | 10+ | 8-9 years | Free | 12,257 USD/year | B1 | Exam / Interview |
| Foundation | 16+ | 1 year | 13,618 USD/year | 15,132 USD/year | B2 | IELTS 5.0 |
| Bachelor's | 17+ | 3-5 years | Free | 16,191 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 / TOEFL 79 |
| Master's | 20+ | 1-2 years | Free | 11,349 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 / TOEFL 83 |
| MBA | 20+ | 1-2 years | 3,026 USD/program | 45,395 USD/program | C1 | IELTS 6.5/ TOEFL 83 / Danish A-level |
| Doctoral | 20+ | 3-4 years | Free | 15,132 USD/year | C1 | IELTS 6.5 / TOEFL 83 |
| Item | Average cost |
|---|---|
| Registration fees | 113 USD |
| Visa | 288 USD |
| Accommodation | 605 USD/month |
| Insurance | 30 USD/month |
| Meals | 257 USD/month |
| Public transportation | 45 USD/month |
All prices and requirements must be checked on the university websites.
Traditional Foundation programs are not so prevalent in Denmark like in countries such as the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. Many of those on offer prepare for certain specialties, for example, for an engineering bachelor's degree. To enter, you need a school certificate and proof of knowledge of English / Danish. The study is aimed at preparing the student in specialized subjects and improving the knowledge of a foreign language. In addition, applicants get used to the education system in the country and to Danish culture. Additionally, there are Pre-Masters programs. For admission, you need a bachelor's degree and a certificate of proficiency in a foreign language (English or Danish).
As an alternative to Foundation, in Denmark there are programs of Higher Preparatory Examination (HF). They last for 2 years and are aimed at preparing for higher education. There are required subjects (mathematics, science, etc.), electives, Danish and English. For admission, 9-10 years of secondary school are required. The Danish Agency for Science and Higher Education evaluates the diploma for equivalence to the local one, and the final word on the admission of a foreign applicant remains with the director of the program / school[7].
In addition, there are many summer schools in Denmark. As a rule, they teach in English. There, both Danes and foreigners study. Courses are offered at different levels and within different areas of specialization, for example, in economics, law, tourism. Here you can find a list of summer schools.
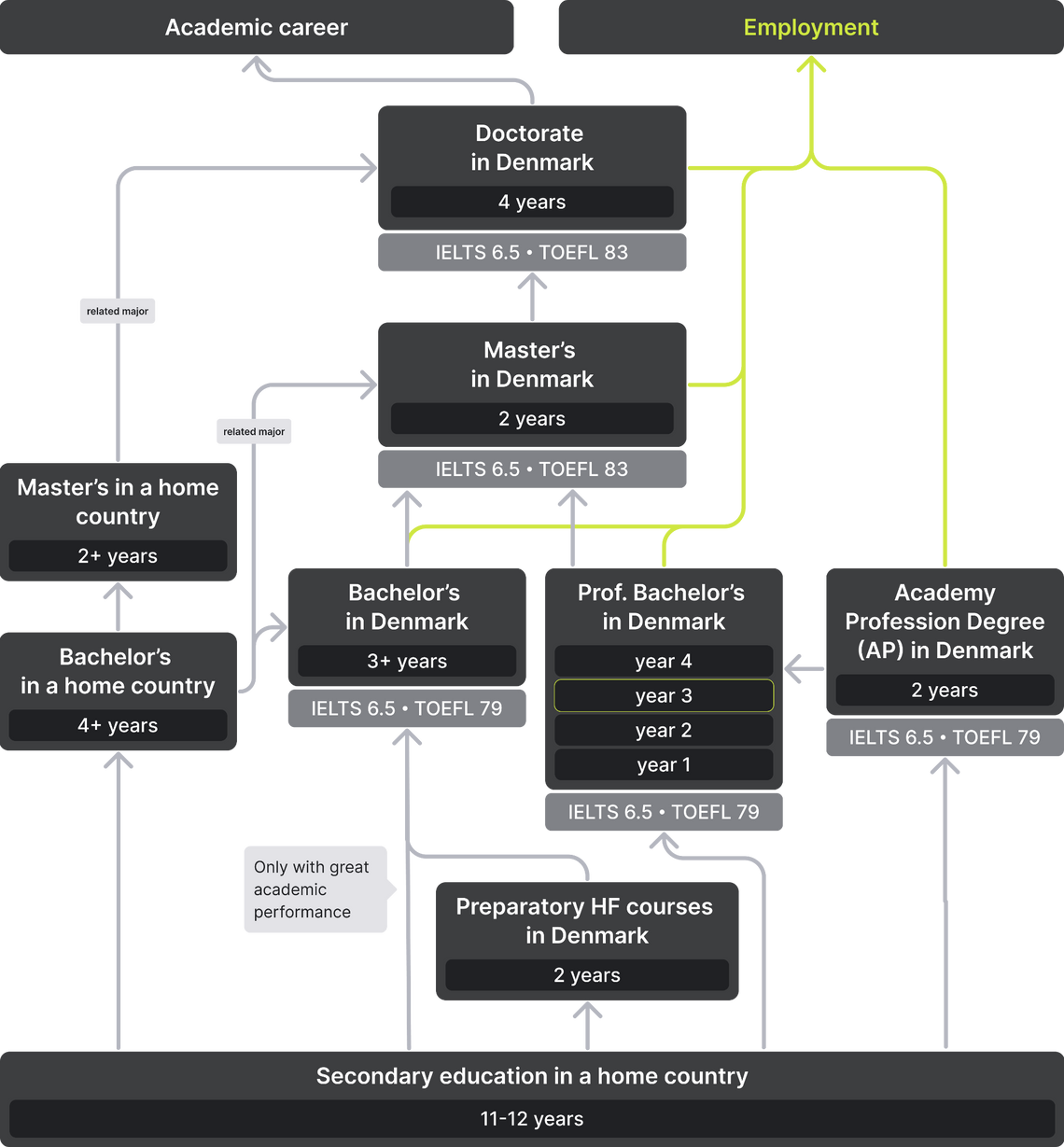
Vocational education exists in Denmark in the form of Academy Profession degrees (erhvervsakademigrad, AP). They are awarded after 1.5-2.5 years of study (90, 120 or 150 ECTS) and include compulsory employment lasting at least 3 months (15 ECTS). Most of the programs are designed for 2 years (120 ECTS) and are equivalent to 2 years of bachelor's program — in a way it is an analogue of the Associate's degree in the US, Canada, the Netherlands and some other countries. Teaching combines theory and practice. Professional programs are offered in the following disciplines: business and economics, technology, IT, laboratory technology, marketing, chemistry, biotechnology and social sciences, management, tourism, media, design and healthcare.
For admission, you will need:
Business academies and university colleges implement erhvervsakademigrad (AP). Graduates of certain specialties can continue their education at a professional bachelor's degree (takes 1.5 years) or go to work. Here you can find professional programs.
In Denmark bachelor's degree is represented by:
After completing any bachelor's degree, young specialists can continue their higher education or start looking for work in a profession.
A master's degree (masteruddannelse) is awarded after 2 (in some cases 3) years of study (60 ECTS and 90 ECTS, respectively). Some Master's programs are longer, such as Medicine — 3 years (180 ECTS) and Veterinary Medicine — 2.5 years (150 ECTS). The Master's degree is only available at universities and in higher education institutions of arts and architecture at the university level.
The curriculum consists of compulsory subjects, electives and thematic courses. The main teaching method is problem-based learning. Students attend seminars and lectures, solve theoretical and practical assignments, work in groups and individually, as well as undergo internships and participate in exchange programs. At the end of their studies, master’s students submit a dissertation, which they work on for 6-9 months in teams or independently.
There are 2 types of doctoral studies (PhD), which usually last 3 years:
The latter is a project in the area of the company's interests. The student is simultaneously enrolled in the university and hired by the company as an employee. The system was developed for cooperation between companies and universities and promotion of research and development in Danish industry.
Study in PhD programs (180 ECTS) consists of taught courses and independent research. Within 3 months, the student and the academic supervisor create a curriculum and research project, which the university reviews and approves. The curriculum should include 6-month courses related to the research topic. PhD candidates additionally teach and/or share research results (dissertation) through presentations and publications.
Often, Danish universities send students to foreign universities or to production, so that the resulting scientific work is multifaceted and fundamental. PhD candidates defend their dissertations not only in front of academicians of the alma mater, but also in front of foreign professors and expert practitioners.
Often, PhD candidates look for funding and scholarships that cover tuition fees, book costs, travel expenses, etc. Sometimes universities and other organizations pay salaries to doctoral students (studentships). You can look for scholarships in universities, research centers, private foundations and enterprises. It should be noted that the competition for PhD in Denmark is high. Current opportunities can be found here and here.
Academic career in Denmark begins with positions of Assistant Professor / Researcher, which last for approximately 4 years. The main duties of an Assistant Professor are research (publications) and teaching. Researcher conducts research, teaches and sometimes gives scientific advice to the public sector. Usually these are temporary full-time positions. To obtain a permanent contract, you must successfully complete an intensive evaluation period, which takes place during the last 6 months of the fixed-term contract.
The next positions are Associate Professor / Senior Lecturer, and then Professor. These are permanent. The university can offer especially talented Associate Professors / Senior Researchers promotions to a Professor status, if they have international recognition and research. Other qualifications may also be required, such as knowledge and technology transfer, patenting and collaboration with external partners. There are also positions: Research Assistant, Teaching Assistant, Teaching Assistant Professor / Teaching Associate Professor, Teaching Assistant Professor, Teaching Associate Professor, Part-time Lecturer, etc.
Teaching experience and a good track record of research are required to advance the career. The Danish educational system is open to foreign scholars. It is desirable to know Danish, but since universities offer English-language programs, and the teachers and university administration speak English, not knowing the official language will not be an obstacle. Universities sometimes pay foreign professors more than local professors, and additionally help especially talented scientists with travel expenses. Salaries at the Danish academy range from 49,934 USD to 93,816 USD per year before tax removal.
EU/EEA or Swiss citizens can work in Denmark with no restriction.
For other nationals, in addition to the student residence permit, a limited work permit is issued (sticker in the passport). If you did not apply for it during the registration of the residence permit, you can obtain permission from the Danish Immigration Service. Students are allowed to work:
If you are under 18, you need a written job offer or contract for a specific position. The employer must also register with the Danish Immigration Office. The limited permit is additionally valid for 6 months after completing a full education program in Denmark. This time is essentially given to find a permanent job.
Working more than 20 hours is illegal and may result in a warning, a fine, cancellation of a residence permit, deportation, and even incarceration.
Read more about working conditions in Denmark here.
Finding a job in Denmark is not always easy, especially without knowing the language. Some international students find jobs in bars or restaurants. Others distribute newspapers, work as telemarketers or translators. The minimum wage is about 17 USD per hour[8].
Many universities have career centers that help students with job search. In addition, the official Danish website of international recruiting offers information on how to find suitable student work, how to write a resume, and how to pass interviews. Vacancies are also posted on the site.
Nordic, EU/EEA or Swiss citizens are eligible to stay and work in the country after studies without any limitations. However, they still need a registration certificate to live there.
Graduates from non-EU/EEA countries with a student residence permit can only look for work in Denmark for 6 months after graduation. During this time, you can work the same hours as during your studies: 20 hours a week and full time in June, July and August.
There is also an Establishment card, which gives you the right to work full time from the date of application or to run a business. The cardholder can be employed in any company and in any position in Denmark. After hiring, you do not need to apply for a separate permit, or a residence permit if you change jobs.
The Establishment card is issued for 2 years. It can be extended for 1 year if you work in your specialty. To obtain a card, you must:
Cost — 288 USD, application processing — 1 month. Here you can read more about the Establishment Card.
Denmark also has various work permits: for researchers, for shepherds and farmers, startups, Fast-track, etc. Here you can see all the possibilities presented.
To obtain Danish citizenship, you must have an unlimited residence permit and reside in Denmark. The application for Danish citizenship is reviewed by the Ministry of Immigration and Integration. Danish graduates can obtain citizenship after 5 years of continuous residence in Denmark. The main requirement is that education lasted at least 3 years. You can read more information here.
Higher education institutions in Denmark cooperate with business organizations and research institutes. Business meetings, visits to leading companies and internships are organized for students. All this prepares future specialists for professional activities in international companies.
The Danish economy is dominated by the service sector which constitutes for 80% of all jobs, while about 11% of all personnel work is in the manufacturing industry, 2% in agriculture. The main industries are electronics, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food, furniture, fashion, machinery and equipment, tourism, oil and gas. The unemployment rate in the country as of February 2020 was 3.7%[9]. However, finding a job here is not easy. Knowledge of the Danish language and networking can be decisive factors in finding a job.
Diplomas from Danish universities are recognized all over the world, so it is relatively easy for a young specialist to find a job in other countries.
60+ countries
we work with
$1,000,000 saved
by students through scholarships
6,400 offers
our students got